Using the IoT (Internet of Things) For Measurement and Testing in the Railway Industry
The IoT now plays a central role in the world of industry with numerous oportunities…
Developing IoT in our laboratories
The challenges and opportunities are numerous, with the goal being to develop new products and services while also enabling:
- real savings on recurring costs (energy, maintenance, etc.)
- improvement in production quality
EURAILTEST, as an assembler of tailor-made, cutting-edge testing solutions, needs to surround itself with effective, synergistic laboratories brimming with innovation. The IoT challenge is therefore central to the development and innovation projects of our partner laboratories.
The topic of IoT is well-known in the field of maintaining fixed installations and rolling stock, because it is a source of many innovative solutions. The challenge for Eurailtest’s partner laboratories is determining what applications there are for IoT that can lower costs and save time when conducting various railway tests.
The Railway Testing Agency (AEF), the Test and Measurement Laboratory (LEM), and the Measurement and Test Department (DGII ME) all have research and development divisions.
In addition to conducting tests and providing the client with the knowledge and skills needed to make their projects successful, those same experts invest a lot of time and energy in railway technological innovation.
Here are a few applications of IoT developed by our partner laboratories.
The AEF has developed the IoT Box.

Since 2016, the AEF has been internally developing the “IoT Box”, which consists of an electronic device whose purpose is to exchange information for a lower cost, and to bring together sensors, users, networks, and the cloud. Since 2016, the IoT Box has advanced considerably, incorporating the latest network technologies and telecommunication protocols (Lora, RFID).
The AEF’s objectives are:
- Collection of data captured on test trains in order to interpret them without human intervention
- Low system electricity consumption
- Use of self-powered wireless sensors
- Geolocation
- End-to-end control over the data
- Collection of data from different communication protocols.
The AEF continues to develop the IoT Box in order to make it more effective and be able to deploy it across various testing and measurement services.
For its own part, DGII ME has developed the devices SENTINEL and VIBRALERTE.
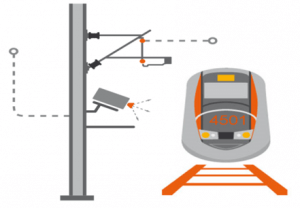
SENTINEL (a French acronym for “Digital Recording System for Electrical Currents and Voltages”) is an industrial device for remotely monitoring electricity distribution stations (electrical traction and signal substations, train station substations, etc.).
The algorithms and processing carried out by the SENTINEL application provide accurate information needed to avoid incidents and abnormal wear to installations, minimize incident impacts, and optimize maintenance and operation.
This system is made up of sensors and acquisition boards packed into a cabinet for fixed installations, or in the form of a mobile briefcase for one-time servicing.
The data is provided on a secure Web platform for different types of user profiles (technical experts, maintenance workers, substation controllers, etc.). It is used to:
- view a substation parameters in real time,
- detect and record disruptive phenomena,
- monitor and alert by reporting alarms (email).
SENTINEL is currently being deployed on the French national rail network (RFN), with 57 substations already outfitted.

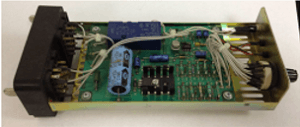
VIBRALERTE
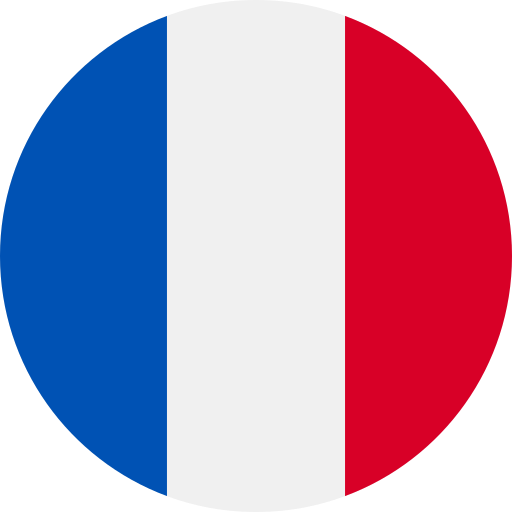
The work carried out on the railway infrastructure may generate vibrations with potential consequences on the operation of the signaling facilities, and therefore railway safety and operation. VIBRALERTE is a device that can preventively warn of a failure in these signaling facilities due to these vibrations.
How does it work?
VIBRALERTE is made up of an electronic box and standard relays, which are representative of the signaling facility being monitored. It triggers an audible and visual alarm whenever it detects a state change in a contact of those relays above a set threshold. The latest version of VIBRALERTE also enables automatic remote transmission (by SMS) of an alert to the designated agents.
VIBRALERTE has been incorporated into numerous RFN modernization operations.
The LEM has conducted several IoT experiments
RATP’s Test and Measurement Laboratory (LEM) has set up several experiments involving IoT. The devices installed include:
- Sensors for collecting raw data
- A network hub and gateway for centralizing the data
- An “IoT management” system for reporting data on the IoT platform
- A “visualization and usage” information system to decipher and make use of the data.
These IoT devices particularly make it possible to measure the following data: Air temperature, humidity, rail temperature, platform incline, track movement, etc.
IoT plays an increasingly important role in railway testing and measurement. Concurrent with these projects and devices that supplement and improve upon traditional measurement methods, digital simulations are also central to research and development within our laboratories.